The term “automation” has become ubiquitous, sparking curiosity and debate alike. But what exactly is automation, and why is it so vital to our modern world? This article aims to shed light on the multifaceted concept of automation, exploring its diverse applications across industries, the pivotal role played by automation professionals, the compelling reasons for its adoption, real-world examples that showcase its transformative power, and the pertinent issue of automation’s impact on employment. By the end of this exploration, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of automation’s far-reaching influence on how we live and work in the 21st century.
Automation Encompasses Many Vital Elements, Systems, and Job Functions. Automation, in its essence, refers to the use of technology to perform tasks with minimal human intervention. It encompasses various elements, systems, and job functions across industries, reshaping the way we work and live.
Why is the Automation Professional So Important?
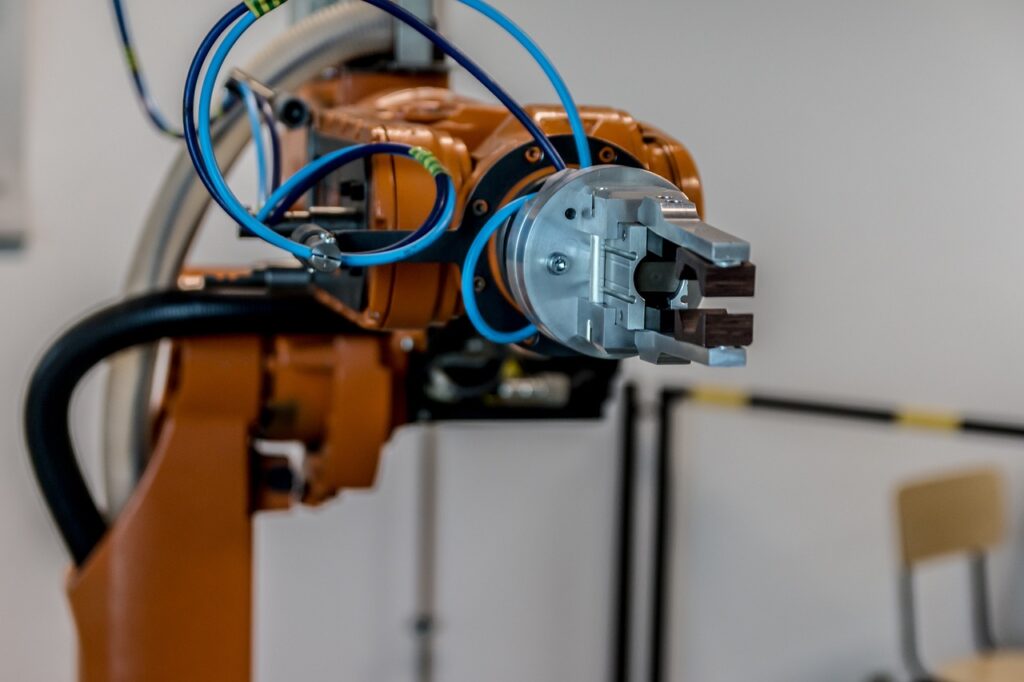
Automation professionals are the architects behind the seamless integration of technology into processes. They design, implement, and maintain automated systems, ensuring efficiency, reliability, and safety. Their expertise is crucial in optimizing operations and achieving desired outcomes.
Why Use Automation?

Automation offers a multitude of benefits that drive its adoption in diverse fields:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Automation streamlines tasks, reducing errors and increasing productivity.
- Consistency and Reliability: Automated systems perform tasks consistently, minimizing variations.
- Cost Savings: Over time, automation can lead to significant cost reductions.
- Safety: In hazardous environments, automation keeps humans out of harm’s way.
- Scale and Speed: Automation enables businesses to scale operations and respond rapidly to changing demands.
Examples of Automation

Automation is pervasive in our daily lives and industries:
- Manufacturing: Robots assemble products with precision and speed.
- Finance: Automated trading algorithms execute complex transactions in milliseconds.
- Healthcare: Robotic surgery systems assist surgeons with precision procedures.
- Agriculture: Autonomous tractors and drones optimize farming operations.
- Transportation: Self-driving vehicles are revolutionizing the logistics industry.
Automation and Job Loss

The adoption of automation has sparked debates about its impact on employment. While automation can replace certain routine tasks, it also creates new roles in designing, maintaining, and overseeing automated systems. The net effect on employment depends on various factors, including the industry and the workforce’s adaptability.
Conclusion
Automation is a transformative force that has already reshaped industries and continues to influence how we work and live. By understanding its principles and harnessing its potential, businesses and individuals can navigate the changing landscape of work and technology, maximizing efficiency and innovation.
FAQs
1. What exactly is automation, and how does it differ from manual processes?
- Automation involves the use of technology to perform tasks with minimal human intervention. It differs from manual processes, where tasks are executed entirely by humans, often involving repetitive actions.
2. Why is the role of an automation professional crucial in implementing automation systems?
- Automation professionals design, implement, and maintain automated systems to ensure they operate efficiently and safely. Their expertise is vital in achieving the desired outcomes and addressing technical challenges.
3. What are some practical reasons for using automation in various industries and sectors?
- Automation offers benefits such as enhanced efficiency, cost savings, improved consistency, safety in hazardous environments, and the ability to scale operations and respond quickly to changing demands.
4. Can automation lead to job loss, and what is its overall impact on employment?
- Automation can replace certain routine tasks but also creates new job opportunities in designing, maintaining, and managing automated systems. The net impact on employment varies by industry and the adaptability of the workforce.
5. What are some real-world examples of automation in everyday life and across different industries?
- Automation is pervasive and can be seen in manufacturing (robotic assembly), finance (automated trading), healthcare (robotic surgery), agriculture (autonomous farming), and transportation (self-driving vehicles), among others.

